Electric bicycle batteries are rechargeable power sources that provide the energy needed to propel the bike using an electric motor. The most common types of batteries used in e-bikes are lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries. These batteries are chosen for their high energy density, relatively low weight, and ability to provide consistent power over extended periods.

The battery in an electric bicycle is one of the most important and expensive parts of the bike. Without it, even with the motor and battery management system on the bike, you’d only get it to go under your own power.
As with anything battery-powered, people are concerned about how far it will go on a charge, as well as how long the battery will last. Around 2016, most of the e-bike batteries had a capacity of 400Wh (Watt-hours, a measure of the amount of energy in the battery) and could usually let you ride 15-25 miles on a full charge. Most e-bikes now, save for the super-light e-bikes, have capacities close to double that, in the 700-900Wh range, which gives you a much longer range.
ADVERTISEMENT
Watt Are You Talking About?
A battery is made of several individual cells. Most e-bike batteries are made from 18650 lithium-ion cells, named 18650 because they measure 18mmx65mm, though some of the higher-end brands opt for 21700 cells (you guessed it, 21mmx70mm/). The larger the individual cell, the more power it can store and then release.
A battery management system, an on-board computer, keeps track of the charging and discharging of each individual cell to make sure they’re all close to the same capacity. That capacity can be expressed in Watt-hours or in Amp-hours.
Think of watt-hours as a measure of the total energy a battery can hold and provide. It takes into account both the amount of power (in watts) that a device uses and the duration (in hours) for which it can use that power.
ADVERTISEMENT
Imagine you have a battery with a certain amount of energy, like a gas tank in a car. Watt-hours tell you how much energy is available to be used. If you have a battery with a higher watt-hour rating, it means you have more energy stored in the battery, which can power devices for a longer time or with more power.
Amp-hours, on the other hand, measure the capacity of a battery in terms of current flow. It indicates how much electric charge a battery can hold and deliver over a specific period. You can think of amp-hours as the size of a bucket that holds electric charge.
Imagine filling up a bucket with water. The amount of water the bucket can hold is like the amp-hour capacity of a battery. If a battery has a higher amp-hour rating, it can hold more charge and therefore provide electricity for a longer time.
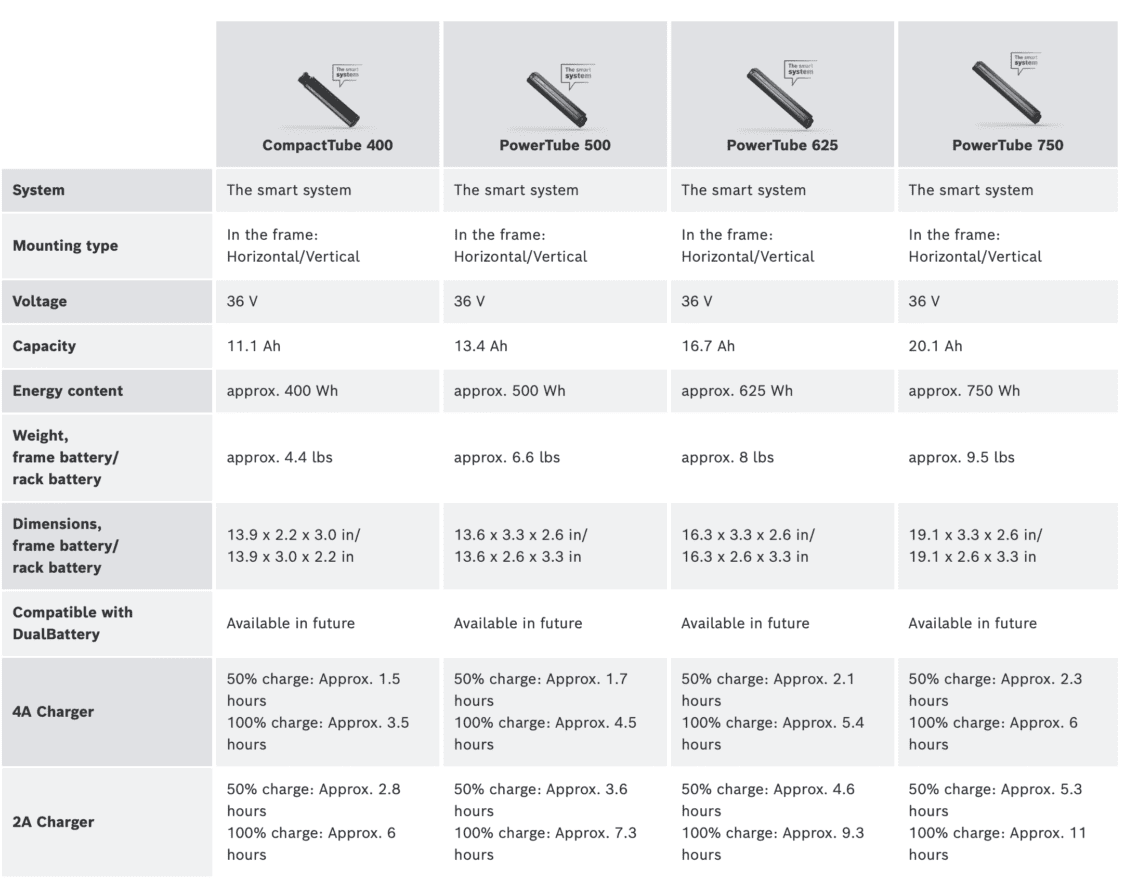
When it comes down to it, I prefer listings of Wh (Watt-hours) as a standard spec for batteries when comparing them. Some manufacturers offer multiple battery sizes for a given bike. For example, some Bosch-powered e-bikes offer a choice between 400Wh, 500Wh, 625Wh or 750Wh. Some bikes even have the option to run two batteries.
Charge Cycles
With the battery and the battery management system clamoring to keep your batteries charged and healthy, there are certain things you can do to absolutely maximize your battery life. Most batteries offer a certain number of charge cycles before the battery loses enough of its capacity to be ready for replacement. This is when the battery’s capacity is at around 80% of what it was new.
At that point, you should recycle the battery and replace it with a new one. There are many bike shops that will take your old battery and send it to a recycling center like Call2Recycle or Redwood Materials.
ADVERTISEMENT
The good news is that most batteries now are rated for at least 500 charge (up to 1000 on some) cycles before that happens. Does this mean that every time you plug in your battery to charge it, that’s one cycle? No. If you charge it from 0% to 100%, that’s a full cycle. If you charge it from 50% to 100%, that’s ½ cycle.
The lifespan of an e-bike battery depends on various factors, including the battery’s chemistry, usage patterns, maintenance, and environmental conditions. On average, a well-maintained lithium-ion battery can last anywhere from 2 to 5 years or around 500 to 1000 charge cycles. However, it’s important to note that the battery’s capacity gradually decreases over time, resulting in reduced range and performance.
Maintaining Your Electric Bike’s Battery Health
There are definitely some good ways to keep your battery healthy for a longer period of time. First, it’s never a good idea to fully drain your battery to 0%. You can cause irreparable damage to it that way. Ideally, never discharge it below 20% (if your display doesn’t show a percentage, but has five bars to indicate the current SOC, recharge when you get to the last bar).
Also, unless you need all the range of the bike for your next trip, only recharge to 80%. Charging to 80% always happens quickly when charging a lithium-ion battery, but then charging slows significantly to protect the battery from overheating. Charging to 80% will definitely be kinder to your battery life.
ADVERTISEMENT
If you’re storing your bike for a long time (e.g. for the winter), store it at about 40% (again, for displays without a percentage shown, that’s 2 out of 5 bars). If you’re storing it for a while, consider storing the bike or at least the battery indoors away from the extreme heat or extreme cold of your garage. Avoid charging the battery in temperatures below freezing or above 100°F (37.8°C).

Remember Robin:
- When storing your bike long-term, keep the state of charge (SOC) at 40%
- Recharge your battery before it reaches 20%
- Charge to 80% instead of 100% when you can
- Keep your bike, or at least the battery, inside when the temperatures are extreme
Don’t Overwork Those Batteries
Make sure you keep your bike properly maintained, checking the chain for proper tension and lubrication, check your brakes, and definitely keep your tires inflated to the proper pressure. Check the sidewall or your bike’s owner’s manual for that information. A tire that’s low makes you and the bike work harder to get moving.
Keeping your bike well maintained and taking care of your battery will get you many years and many thousands of miles of fun rides, commutes, shopping trips and everything else you enjoy on your bike.
Now keep it rubber-side down and go ride!
ADVERTISEMENT

FEATURE IMAGE: TONY DONALDSON
FTC: We use income-earning auto affiliate links. Learn more.










