- Renewable resources reached a record-breaking 30% of global electricity production in 2023.
- Fossil fuels used for electricity generation globally have decreased from 64.7% in 2000 to 60.6% in 2023.
- The International Energy Agency (IEA) urges governments to increase renewable energy to reach a Net Zero Emissions (NZE) Scenario by 2050.
The year 2023 marked an unprecedented shift in how the planet generates electricity, with a boom in wind and solar energy pushing renewable resources to account for a record-breaking 30% of global electricity production. This surpassed previous records, including under 19% in 2000, as Ember’s Global Electricity Review reported.
ADVERTISEMENT
Global levels of planet-heating pollution hit a record high in 2023. The increased adoption of renewable energy has been instrumental in driving down the electricity sector’s carbon intensity, which measures carbon dioxide pollution produced per unit of electricity. This carbon intensity reached a record low in 2023, showing a 12% reduction from its peak in 2007.
The growth of fossil fuel usage has decelerated by almost two-thirds over the last decade. More than half of the world’s countries are five years past their peak usage of fossil fuel-generated electricity. The share of fossil fuels decreased from 64.7% in 2000 to 60.6% in 2023. Ember projects a steeper decline to 57.6% by 2024.
Solar Is Booming
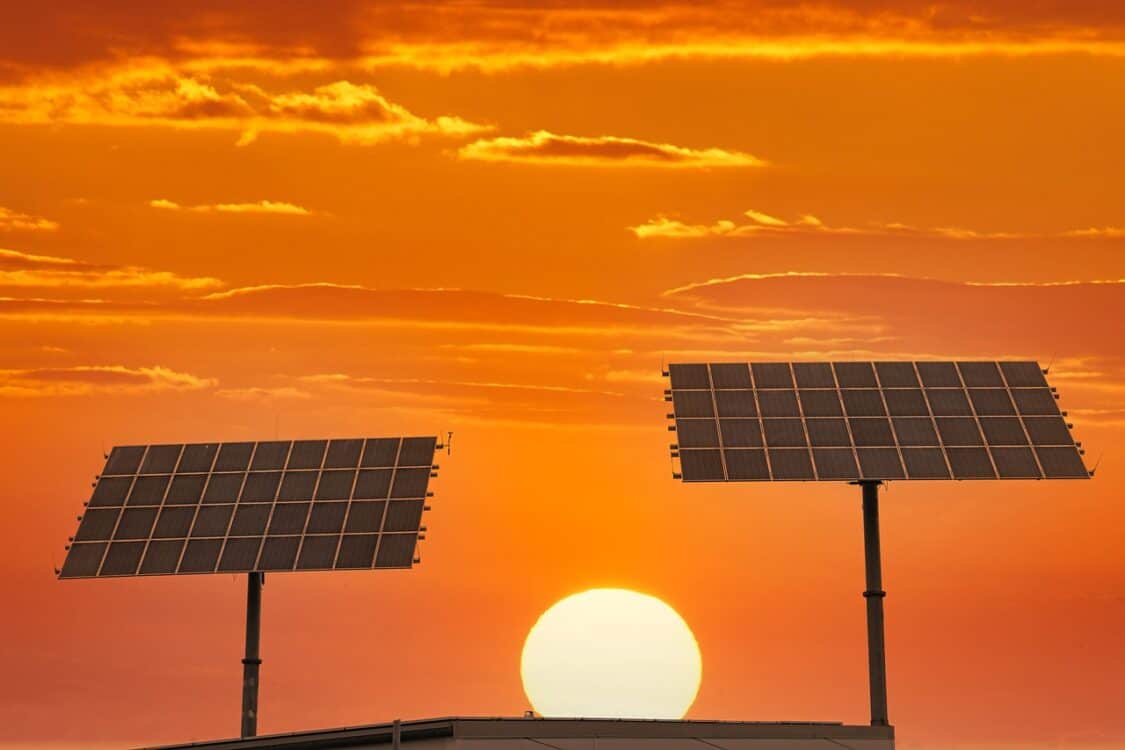

Solar energy was the fastest-growing global source of electricity in 2023 and the fastest-growing kind of clean energy, marking the 19th consecutive year it has led in expansion. In the U.S., 238,121 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity came from solar in 2023, more than eight times the amount reported in 2014, according to Climate Central.
The Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) predicts that solar will contribute 30% of U.S. electricity by 2030, after it added a record-breaking 32.4 gigawatts (GW) of electric generating capacity in 2023.
Solar power also has the bonus of being the most eco-friendly way to power electric vehicles.
ADVERTISEMENT
China Is the Largest Producer of Solar Electricity
China remained the largest producer of solar energy worldwide in 2023. The country was responsible for more than one-third of the global solar generation this year, producing over twice the amount of solar electricity produced by the U.S. Despite these impressive figures, the share of solar power in the electricity mix of both countries stands at approximately 6%.
Solar energy plays a much more significant role in nations like Chile, where it represents 30% of the annual electricity generation, or Australia and the Netherlands, both at 17%. Even California — a state whose economy ranks as the world’s fifth-largest — has 28% of its electricity coming from solar power.
Electricity Demand Is Expected to Soar

Global electricity demand surged to a record high in 2023, equivalent to adding Canada’s current demand. While this upswing extends the trend of rising global electricity consumption, it’s noteworthy that the pace of growth has decelerated compared to the previous decade’s average.
U.S. Electricity Usage Dropped in 2023, Despite 3.3 Million EVs On the Road
Edmunds reported that according to an Experian Automotive Market Trends report from the fourth quarter of 2023, there were about 3.3 million electric cars on the road in the U.S. at the end of 2023. All of the new EVs hitting the road had many people concerned if the electric grid could handle the added capacity needed by EV charging. The grid has handled EV charging just fine so far, thanks to increases in efficiency.
U.S. electricity usage declined from 4067 terawatt-hours in 2022, to 4000 terawatt-hours in 2023, according to Statista.
ADVERTISEMENT
In the United States, the heightened efficiency of electrical appliances and consumers implementing more of these appliances caused a decline in electricity usage in 2023. This decline was despite all the added usage from EV charging. However, with millions more EVs on the way, experts recommend U.S. power grid expansion, upgrades, and modernization.
IEA’s Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE) Scenario Urges Stronger Support of Renewable Resources
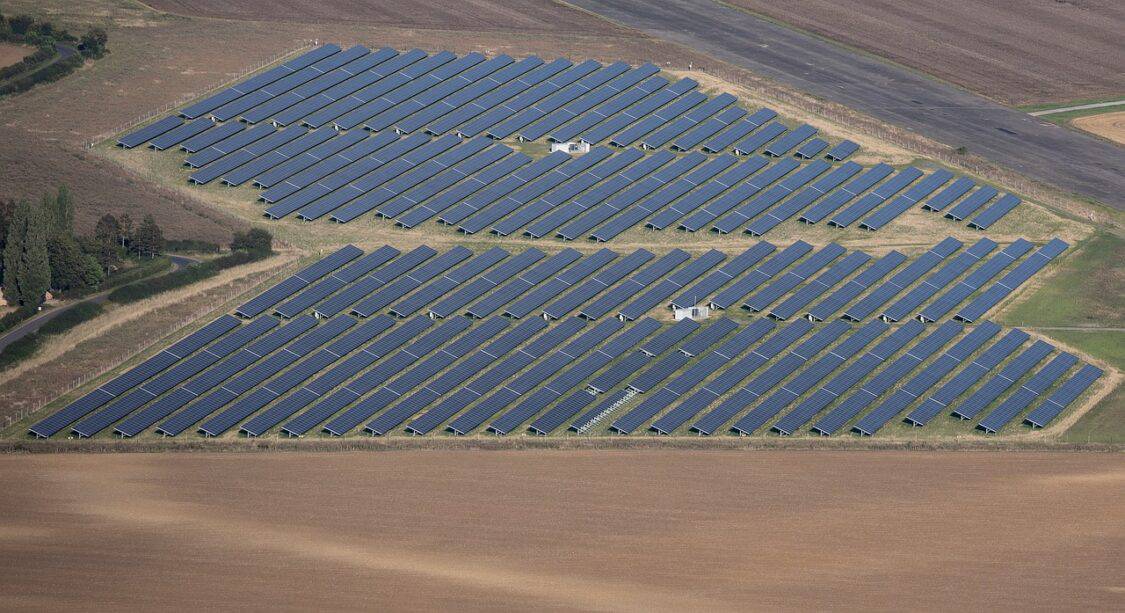

The International Energy Agency (IEA) urges governments worldwide to rally behind five pillars of action addressing the urgent needs of our planet’s energy future. One of the most critical objectives is to triple global renewable power capacity by 2030. This goal envisions elevating renewable capacity in the power sector from 2022 levels to over 11,000 gigawatts.
Under existing policies and market conditions, IEA forecasts predict that global renewable capacity will reach 7,300 GW by 2028, falling short of the IEA’s ambitious tripling target.
While the rise in renewable energy is encouraging, climate leaders such as the IEA say accelerated and concerted efforts from all stakeholders to harness the full potential of renewable energy sources are needed to fight climate change.
We support growth in renewable energy and EV adoption. Growth in renewable resources, new and used EV sales, EV conversions, and other environment-supporting measures such as a circular economy ensures a brighter future for us all.
ADVERTISEMENT

FEATURE IMAGE: BRU-NO
FTC: We use income-earning auto affiliate links. Learn more.





















One Response